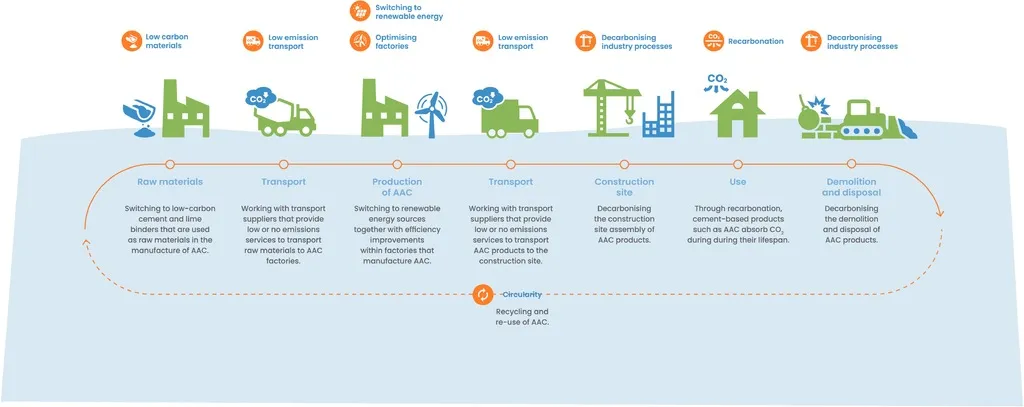
In the quest for sustainable construction, Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) has emerged as a frontrunner, offering lightweight, thermally insulating, and fire-resistant properties with a lower environmental footprint. However, as more AAC-based structures reach the end of their lifespan, the challenge of recycling this material has come to the forefront. A recent study published in the journal *Buildings* sheds light on the current state of AAC recycling research, highlighting both the opportunities and hurdles in this burgeoning field.
Led by Shuxi (Hiro) Wang from the School of Engineering at RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia, the study conducted a scientometric review of AAC recycling research from 2014 to 2024. Utilizing the Web of Science database and bibliometric tools like CiteSpace, Wang and his team identified key trends, techniques, and knowledge gaps in the recycling of AAC.
One of the primary challenges identified in the study is the high energy consumption associated with current recycling methods. “The energy demands of recycling AAC are significant, which somewhat undermines the material’s sustainability credentials,” Wang explained. Additionally, the study found that practical implementation of recycling techniques is limited, and there is a lack of standardized protocols for the recovery of AAC waste.
Despite these challenges, the research also points to several emerging pathways that could revolutionize AAC recycling. These include detailed material characterization, the development of recycling standards, innovative reuse techniques, and the integration of recycled AAC in new construction. “Hybrid material systems, where recycled AAC is combined with other materials, show particular promise,” Wang noted.
The study’s insights are crucial for advancing sustainable building material strategies and informing policy and practice in construction waste management. For the energy sector, the findings could drive the development of more energy-efficient recycling technologies, reducing the overall environmental impact of AAC use.
As the construction industry continues to prioritize sustainability, the recycling of AAC will play a pivotal role in achieving circular economy goals. Wang’s research provides a comprehensive foundation for future developments, encouraging stakeholders to invest in and adopt innovative recycling techniques.
Published in *Buildings* (which translates to “Buildings” in English), this study serves as a call to action for the construction industry to embrace sustainable practices and invest in the future of AAC recycling. By addressing the identified challenges and leveraging emerging opportunities, the industry can significantly enhance its environmental performance and contribute to a more sustainable built environment.