In the world of construction and energy efficiency, rigid polyurethane foams (RPUFs) have long been a go-to material, prized for their lightweight nature and exceptional thermal insulation properties. However, their Achilles’ heel has always been their flammability, posing significant safety risks and limiting their widespread application. Enter Qinhe Guo, a researcher from the Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Functional Materials and Applications at Xiamen University of Technology, who is spearheading a critical review of advances in flame-retardant coatings for RPUFs, published in the journal *Fire* (which translates to *Fire* in English).
Guo’s work delves into the challenges and innovations surrounding flame-retardant coatings for RPUFs. Traditional methods of incorporating flame retardants into the foam matrix have often led to compromised mechanical integrity and other issues. “The long-term stability, scalability, and durability of surface flame-retardant coatings for RPUFs remain underexplored,” Guo notes, highlighting a critical gap in the current research landscape.
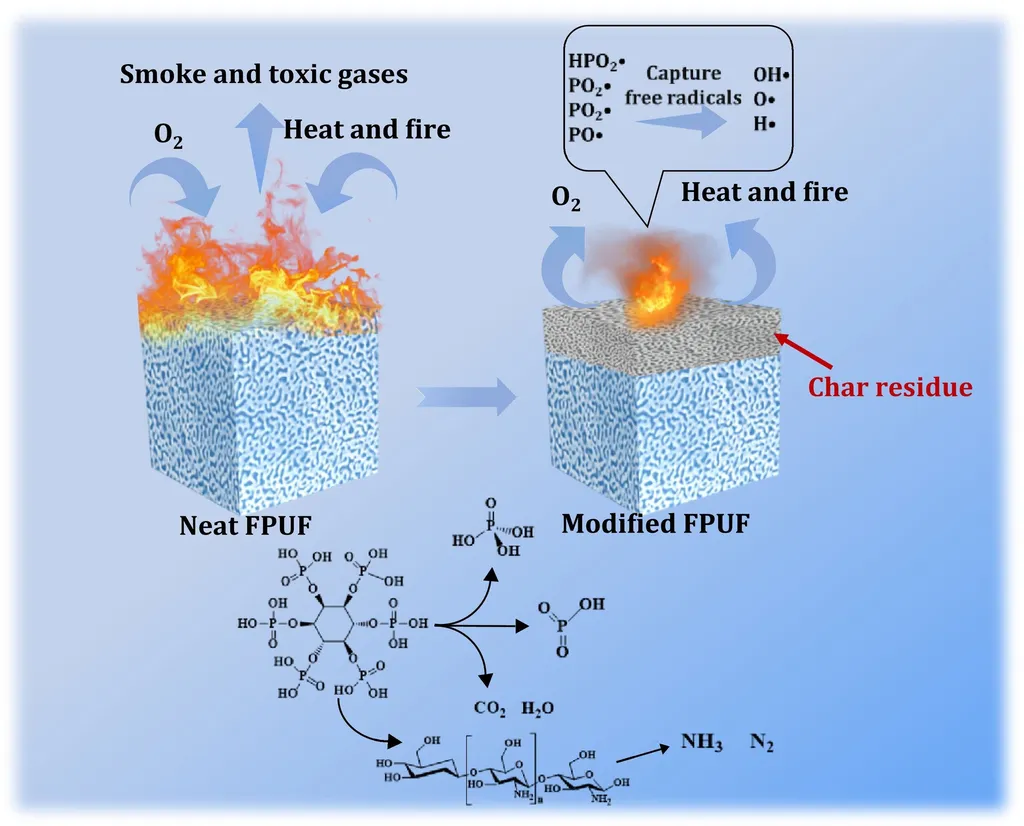
The review explores recent advances in surface-engineered flame-retardant coatings, including intumescent systems, inorganic–organic hybrids, bio-inspired materials, and nanostructured composites. These coatings form protective interfaces that inhibit ignition, restrict heat and mass transfer, promote char formation, and suppress smoke without altering the intrinsic properties of RPUFs. “These developments demonstrate the potential of surface-engineered coatings to achieve high-efficiency flame retardancy while preserving thermal and mechanical performance,” Guo explains.
Emerging deposition methods, such as layer-by-layer assembly, spray coating, ultraviolet (UV) curing, and brush application, enable precise control over thickness, uniformity, and adhesion, enhancing durability and multifunctionality. Integrating bio-based and hybrid approaches further offers environmentally friendly and sustainable solutions.
The implications for the energy sector are profound. RPUFs are widely used in construction, refrigeration, and transportation, where thermal insulation is crucial. Enhancing their flame retardancy without compromising their thermal and mechanical properties can significantly improve safety standards and open up new avenues for their application. “This research provides a pathway for safe, multifunctional, and industrially viable RPUFs,” Guo states, underscoring the potential impact of these advancements.
As the construction and energy sectors continue to evolve, the need for materials that are not only efficient but also safe becomes increasingly paramount. Guo’s review offers a comprehensive look at the current state and future potential of flame-retardant coatings for RPUFs, paving the way for innovations that could redefine industry standards. With the insights gleaned from this research, the future of RPUFs looks brighter—and safer—than ever before.