In the quest for sustainable construction materials, a groundbreaking study published in *Pre-stressed Technology* (预应力技术) is shedding light on the potential of carbon nanotube fibers to revolutionize the crack resistance of geopolymers. This research, led by Qirun Lu, offers a promising avenue for enhancing the performance of geopolymers, a low-carbon alternative to traditional cement.
Geopolymers have long been touted for their environmental benefits, consuming less energy and producing fewer carbon emissions compared to traditional cement. They also offer a solution for reutilizing industrial solid waste, making them a prime candidate for sustainable construction. However, their inherent brittleness and poor crack resistance have limited their structural applications.
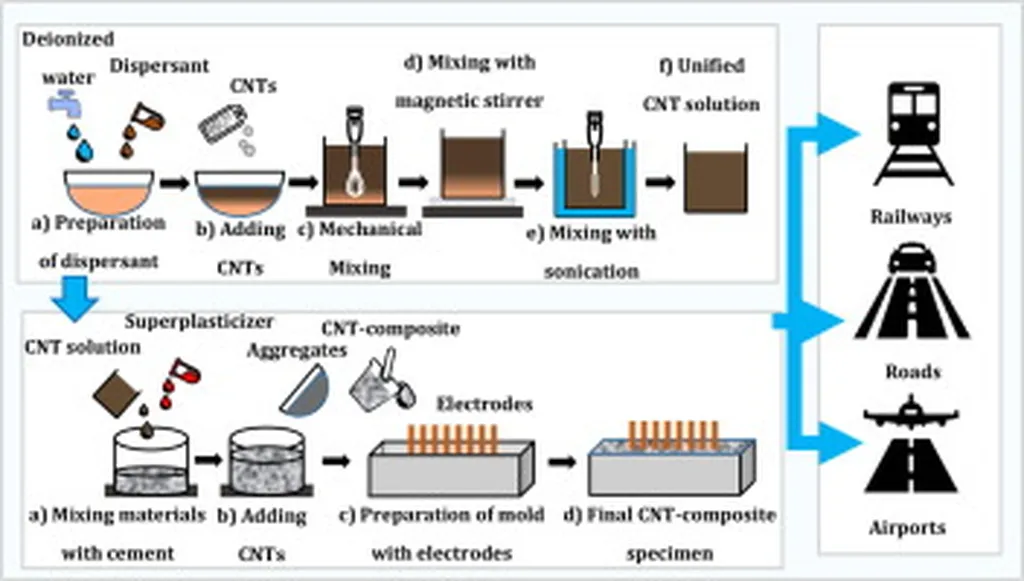
Enter carbon nanotube (CNT) fibers. Known for their exceptional mechanical properties, CNTs are being explored as a means to address these limitations. According to Lu’s research, the incorporation of CNTs significantly improves the crack resistance and mitigates the brittleness of geopolymers. “The optimal overall performance is frequently reported at CNT dosages between 0.12 wt.% and 0.14 wt.%,” Lu explains. This finding provides a crucial theoretical foundation for the practical engineering of CNT-reinforced geopolymers.
The implications for the energy sector are substantial. As the world shifts towards greener construction practices, the development of sustainable materials that can withstand structural stresses is paramount. CNT-reinforced geopolymers could potentially reduce the carbon footprint of construction projects while enhancing the durability and longevity of structures.
This research not only contributes to the scientific community’s understanding of geopolymers but also paves the way for future developments in sustainable construction materials. As Lu’s work continues to gain traction, it is likely to inspire further innovation in the field, driving the energy sector towards a more sustainable future.
The study, published in *Pre-stressed Technology*, marks a significant step forward in the quest for sustainable construction materials. As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change, such advancements are crucial in shaping a greener, more resilient future.