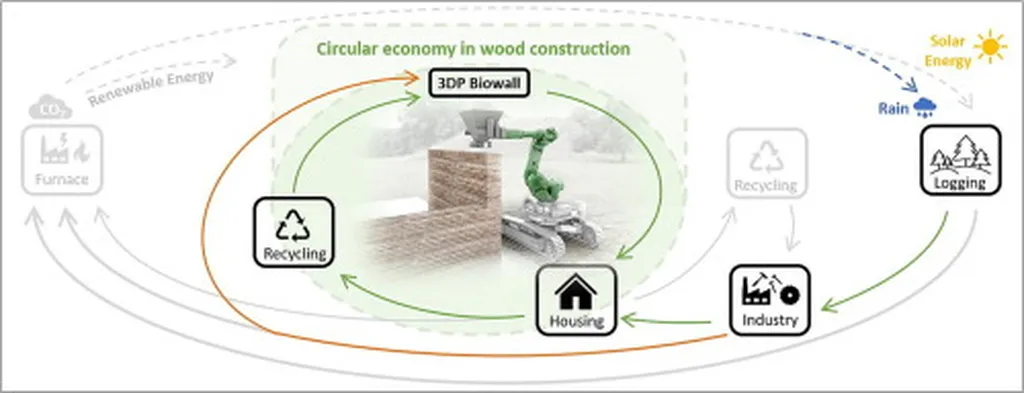
In a groundbreaking study published in the *International Journal of Sustainable Engineering* (translated as *Tidskrift för Hållbar Teknik*), researchers have unveiled a novel framework that could revolutionize the timber construction industry by integrating digital innovations with circular economy strategies. The study, led by F. Lindblad from the School of Business and Economics at Linnaeus University in Växjö, Sweden, offers a roadmap for enhancing material reuse and life-cycle optimization in timber construction, with significant implications for the energy sector and beyond.
The research, which reviewed 110 sources from 2020 to 2025, focuses on how digital technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM), digital twins, the Internet of Things (IoT), material passports, blockchain, and artificial intelligence (AI) can enable circular economy practices like modular prefabrication, design for disassembly, and adaptive reuse. These practices are particularly relevant to the energy sector, where sustainable construction methods can reduce environmental impact and improve energy efficiency.
“Digital infrastructure can greatly enhance material reuse and life-cycle optimization when supported by enabling policies and business models,” Lindblad explained. The study introduces the Digital Circularity Alignment Model (DCAM), a framework that aligns technology, business models, and governance to mainstream circular construction. This model is expected to accelerate the adoption of digital circularity in timber construction, particularly in Europe and North America.
The research identifies several persistent barriers to adoption, including data interoperability and policy gaps. However, it also highlights key enablers such as standardized data protocols and circular procurement policies, which are priorities for future research and practice. “Our analysis suggests that digital infrastructure can greatly enhance material reuse and life-cycle optimization when supported by enabling policies and business models,” Lindblad added.
The findings offer an integrated perspective and roadmap to accelerate digital circularity in timber construction, with significant commercial impacts for the energy sector. By enhancing material reuse and life-cycle optimization, the DCAM framework could lead to more sustainable and efficient construction practices, reducing environmental impact and improving energy efficiency.
This research is a significant step forward in the field of sustainable construction, offering a comprehensive framework that could shape future developments in the industry. As the construction sector continues to evolve, the integration of digital technologies and circular economy strategies will be crucial in achieving sustainable and efficient construction practices.