In the rapidly evolving landscape of smart technologies, universities are increasingly becoming testbeds for innovations that could reshape urban management and energy efficiency. A recent study led by E. G. V. de Jesus from the Geosciences Institute at the Federal University of Bahia (UFBA) in Brazil is making waves in this arena. The research, published in ‘The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences’—translated to English as ‘The International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences’—focuses on the implementation of a smart campus through 3D database modeling, offering a blueprint for more efficient university management and, by extension, urban planning.
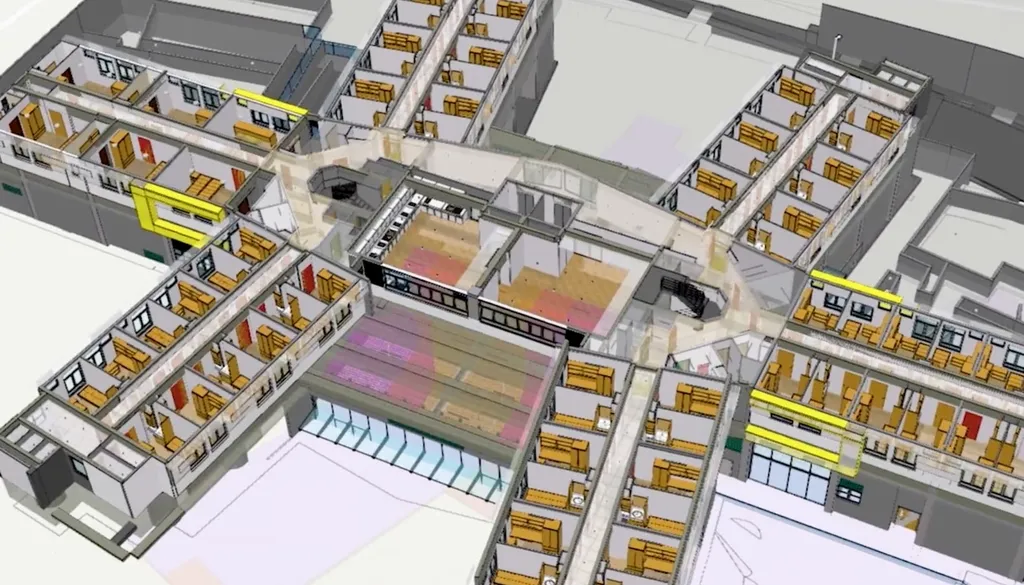
De Jesus and his team have harnessed the power of 3D Geographic Information Systems (3D GIS) to create a comprehensive database model that integrates geometric and semantic data. This approach allows for a detailed and dynamic representation of university campuses, enabling better decision-making and resource management. “The goal is to provide a more transparent and precise view of the needs and challenges of a university campus,” de Jesus explains. “By storing data such as space uses and functions in a 3D database, we can assist university management in making informed decisions that enhance efficiency and sustainability.”
The research highlights practical cases from universities in Brazil and abroad, with a particular focus on the Federal University of Bahia (UFBA). By using CityGML as the standard for creating geometric and semantic models and 3DCityDB to store the campus building models, the study demonstrates the tangible benefits of these technologies. “This approach not only improves the management of university facilities but also contributes to the development of a smart campus that can serve as a model for other institutions,” de Jesus adds.
The implications of this research extend beyond academia. The energy sector, in particular, stands to gain from the insights derived from 3D database modeling. By understanding the spatial and functional dynamics of university campuses, energy providers can optimize their services, reduce waste, and enhance sustainability. “The data collected can inform energy-efficient practices, such as optimizing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, and integrating renewable energy sources,” de Jesus notes.
As universities continue to adopt smart technologies, the potential for commercial impact grows. The ability to manage resources more effectively and make data-driven decisions can lead to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency. This research not only paves the way for smarter campuses but also sets a precedent for urban planning and energy management in the broader context.
In the words of de Jesus, “The future of smart campuses lies in the integration of advanced technologies that provide a holistic view of the environment. This approach can transform not just universities but entire cities, making them more sustainable and resilient.”
As the world moves towards a more interconnected and data-driven future, the insights from this research could shape the development of smart cities and energy-efficient practices, offering a glimpse into the potential of 3D database modeling in transforming urban landscapes.