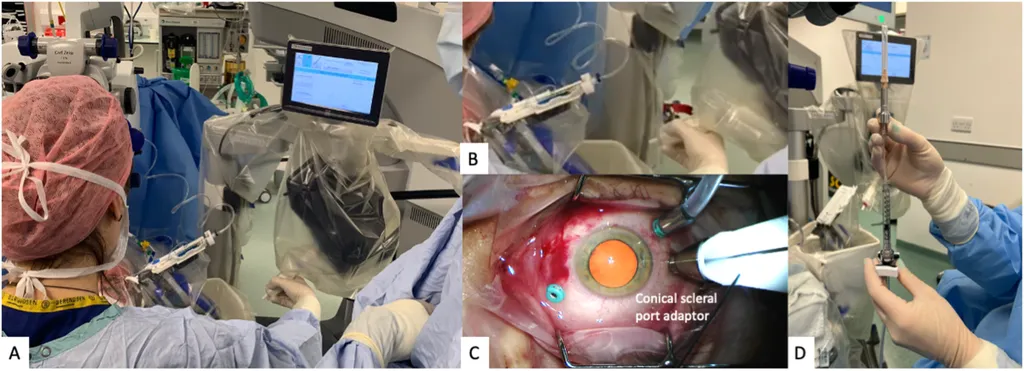
In the delicate world of eye surgery, precision is paramount. A team of researchers, led by Chunbo Wang from the State Key Laboratory of Robotics and System at Harbin Institute of Technology in China, has developed a groundbreaking ophthalmic surgical robot that promises to revolutionize the way retinal diseases are treated. This innovative system, equipped with a force-sensing microneedle and a flexible joint, is set to enhance the accuracy and safety of subretinal injections (SI), a critical procedure for delivering therapeutic agents directly into the subretinal space (SRS).
Subretinal injection is recognized as one of the most effective methods for treating retinal degenerative and genetic diseases. However, the procedure is notoriously challenging due to the constrained intraocular conditions, limited visualization, lack of tactile feedback, and the fragility of retinal tissues. These factors significantly increase the risk of surgical complications and potential vision impairment. “The current manual methods are highly dependent on the surgeon’s skill and experience,” Wang explained. “Our robotic system aims to standardize and enhance the precision of this delicate procedure.”
The robotic system developed by Wang and his team provides precise needle-tip pose control and real-time puncture force feedback. This advanced technology enables force-guided autonomous retinal puncture, ensuring accurate and consistent drug delivery into the SRS. The system’s capabilities were validated through comparative experiments conducted on live Bama pigs, demonstrating its superiority over manual SI techniques. The robotic system achieved more stable puncture trajectories, smoother insertion velocities, precise insertion depths, and a greater than 90% reduction in average puncture force, even in the presence of respiratory and cardiac-induced disturbances.
The implications of this research are profound, particularly for the energy sector, where advancements in medical technology can lead to a healthier, more productive workforce. “By reducing the risk of iatrogenic retinal injury and enhancing the effectiveness of drug delivery, our robotic system can improve patient outcomes and reduce the overall cost of treatment,” Wang noted. This technology has the potential to set a new standard for ophthalmic surgeries, making them safer and more accessible to a broader range of patients.
The research was recently published in the *International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing*, which translates to the *Journal of Extreme Manufacturing Technology* in English. This publication underscores the significance of the work and its potential to shape future developments in the field of robotic microsurgery. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more sophisticated systems capable of performing increasingly complex surgical procedures with unparalleled precision and safety.
The development of this ophthalmic surgical robot represents a significant step forward in the field of medical technology. By addressing the challenges associated with subretinal injections, Wang and his team have opened up new possibilities for the treatment of retinal diseases. As the technology continues to advance, it is poised to make a substantial impact on the energy sector and beyond, improving patient outcomes and enhancing the quality of life for those affected by retinal degenerative and genetic diseases.