In the rapidly evolving landscape of Industry 4.0, a recent study published in ‘Aptisi Transactions on Technopreneurship’ (translated as ‘Transactions on Technopreneurship’) sheds light on how assembly plants are embracing technological innovations. Led by Muhammad Rehan Anwar from the University of Agriculture Faisalabad (UAF), the research delves into the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, offering insights that could reshape the commercial landscape, particularly in energy-intensive sectors.
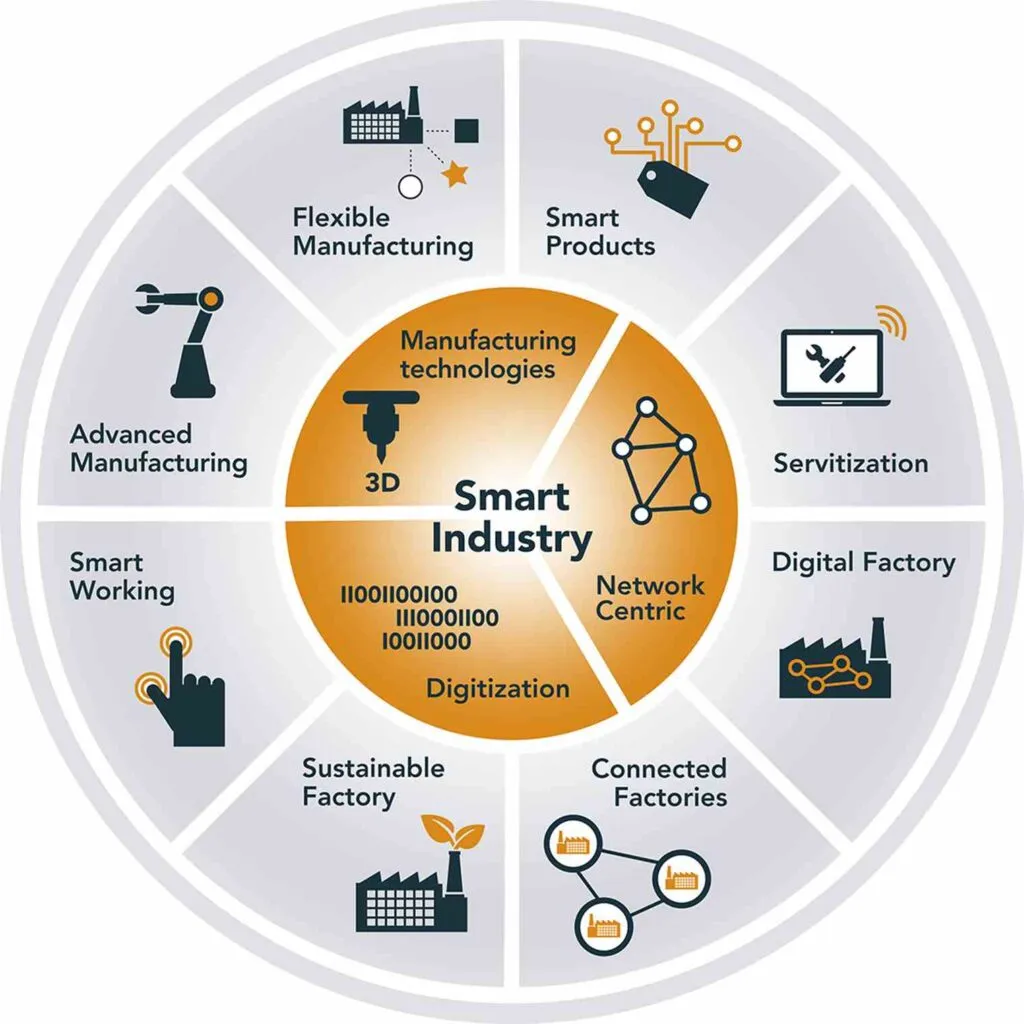
The study categorizes Industry 4.0 innovations into two main areas: front-end and base innovations. Front-end innovations encompass smart manufacturing, smart products, a smart inventory network, and smart work. Base innovations include the internet of things (IoT), cloud administration, big data, and analytics. Anwar’s research suggests that while front-end innovations, particularly smart manufacturing, are being more readily adopted, base innovations present a significant challenge due to limited knowledge and testing.
“Our findings indicate that Industry 4.0 is closely linked to the fundamental adoption of front-end innovations, with smart manufacturing taking center stage,” Anwar explains. This shift towards smart manufacturing could revolutionize the energy sector by enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. For instance, smart sensors and predictive analytics can optimize energy consumption in assembly plants, leading to substantial cost savings and a smaller carbon footprint.
However, the study also highlights the hurdles in implementing base innovations. “The organization is being put to the test when it comes to implementing base innovations,” Anwar notes. This is particularly relevant for the energy sector, where the integration of IoT and big data analytics can unlock new potentials for energy management and grid optimization. Yet, the lack of familiarity and testing poses a barrier that needs to be addressed.
The research proposes the creation of an Industry 4.0 innovation layer, which could serve as a roadmap for companies looking to navigate the complexities of technological adoption. This layer would not only facilitate the integration of front-end and base innovations but also help in measuring the extent of their adoption and impact on business operations.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the insights from Anwar’s study could be instrumental in shaping future developments. By understanding the nuances of Industry 4.0 innovations, energy companies can make informed decisions that drive efficiency, sustainability, and profitability. The study’s findings, published in ‘Transactions on Technopreneurship’, offer a valuable resource for professionals seeking to stay ahead in the dynamic world of Industry 4.0.