In the quest for sustainable construction materials, a recent study published in *Budownictwo i Architektura* (translated as *Construction and Architecture*) has shed light on the potential of recycled concrete sand (RCS) as a viable alternative to natural sand (NS). Led by Imen Bouldoum from the Laboratory LAG at the University of Chlef, the research explores the impact of replacing varying percentages of NS with RCS on the properties of eco-friendly mortar.
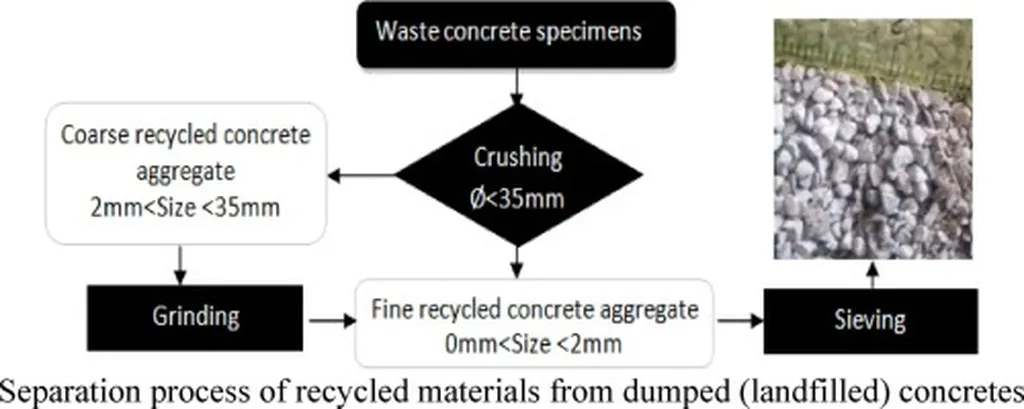
The construction industry’s demand for natural aggregates is ever-growing, while the need to reduce landfill waste from demolition debris is equally pressing. Bouldoum’s study aims to address both issues by investigating the feasibility of using RCS in mortar production. “The main objective was to determine the influence of replacing 20%, 40%, and 60% of natural sand with recycled concrete sand on the mechanical and physical properties of eco-friendly mortar,” Bouldoum explains.
The findings reveal that RCS, which is rich in attached mortar, exhibits lower physical properties compared to NS. It has a lower density, rougher grain shape, and higher water absorption. Despite these challenges, the mechanical behavior of the mortar produced with RCS showed a positive impact on compressive strength. “The presence of RCS has a positive impact on the compressive strength,” Bouldoum notes. However, it was found to have a negative effect on shrinkage, which could influence the durability and long-term performance of the mortar.
The commercial implications of this research are significant for the energy sector, particularly in the construction of energy-efficient buildings. The use of RCS can contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of construction projects, aligning with the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly materials. As the industry moves towards greener practices, the findings from this study could pave the way for more widespread adoption of recycled materials in construction.
Bouldoum’s research not only highlights the potential of RCS but also underscores the need for further investigation into optimizing the use of recycled materials. “This study opens up new avenues for research and development in the field of sustainable construction,” Bouldoum adds. As the construction industry continues to evolve, the integration of recycled materials like RCS could play a crucial role in shaping the future of eco-friendly building practices.
The study, published in *Budownictwo i Architektura*, provides a valuable contribution to the ongoing dialogue on sustainable construction. It offers insights that could influence future developments in the field, encouraging the industry to explore innovative solutions for reducing waste and enhancing the sustainability of construction projects.