In the quest for greener buildings, a novel approach has emerged that could significantly impact the energy sector and reshape how we think about retrofitting existing structures. Xin Bao, a researcher from the School of Civil Engineering at Jilin Jianzhu University in China, has developed an improved grasshopper optimization algorithm that promises to revolutionize multi-objective decision-making in building energy-saving retrofitting design.
The national emphasis on building energy efficiency planning has made it crucial to consider multiple factors when optimizing energy efficiency in existing buildings. Bao’s research, published in the *International Journal of Renewable Energy Development* (translated as *Journal of Renewable Energy Development*), introduces an innovative method to identify the optimal energy renovation strategy for buildings, considering their unique environmental characteristics.
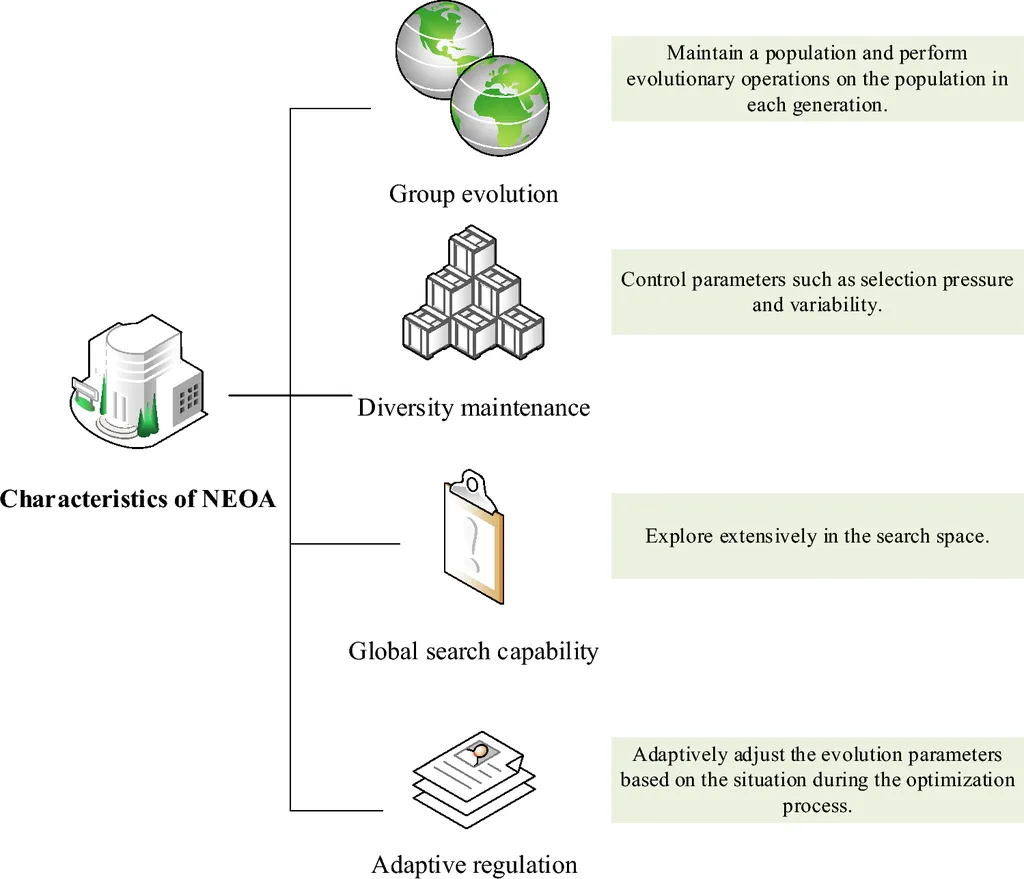
The improved grasshopper optimization algorithm employs an elite inverse strategy approach, enhancing the decision-making process for building renovation measures. “This algorithm allows us to consider various factors simultaneously, such as energy reduction, cost, and environmental impact, to make more informed decisions,” Bao explained.
The results of Bao’s study are promising. The improved grasshopper optimization algorithm achieved a decision accuracy of 98.8% for test samples, outperforming the particle swarm optimization algorithm by 5.5%. Moreover, the algorithm demonstrated excellent repeatability and convergence, indicating its effectiveness for multi-objective optimization.
The practical implications of this research are substantial. By applying the improved grasshopper optimization algorithm to building energy-efficient renovation planning, Bao’s team reduced the power consumption of the renovated power supply system by 23.7% to 49.6%. This not only improves the energy efficiency of buildings but also presents a significant opportunity for the energy sector to reduce consumption and enhance sustainability.
The commercial impacts of this research are far-reaching. As buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption, the adoption of this algorithm could lead to substantial energy savings and cost reductions for property owners and managers. Additionally, the energy sector can benefit from the increased demand for energy-efficient solutions and technologies.
Bao’s research also opens up new avenues for future developments in the field. As the world continues to grapple with climate change and the need for sustainable solutions, the improved grasshopper optimization algorithm offers a promising tool for optimizing energy efficiency in buildings. “This algorithm can be further refined and applied to other areas of energy optimization, contributing to a more sustainable future,” Bao added.
In conclusion, Xin Bao’s improved grasshopper optimization algorithm represents a significant advancement in building energy-saving retrofitting design. Its ability to consider multiple objectives simultaneously and achieve high decision accuracy makes it a valuable tool for the energy sector and a promising direction for future research. As the world continues to prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency, this innovative approach could play a crucial role in shaping the future of building design and energy consumption.