In a world where wireless connectivity is ubiquitous, a team of researchers has found a way to turn the ever-present Wi-Fi signals into a viable energy source. This innovation, detailed in a recent study published in the Journal of Engineering Sciences (JES), could revolutionize the way we power low-energy devices, from wireless sensors to Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets.
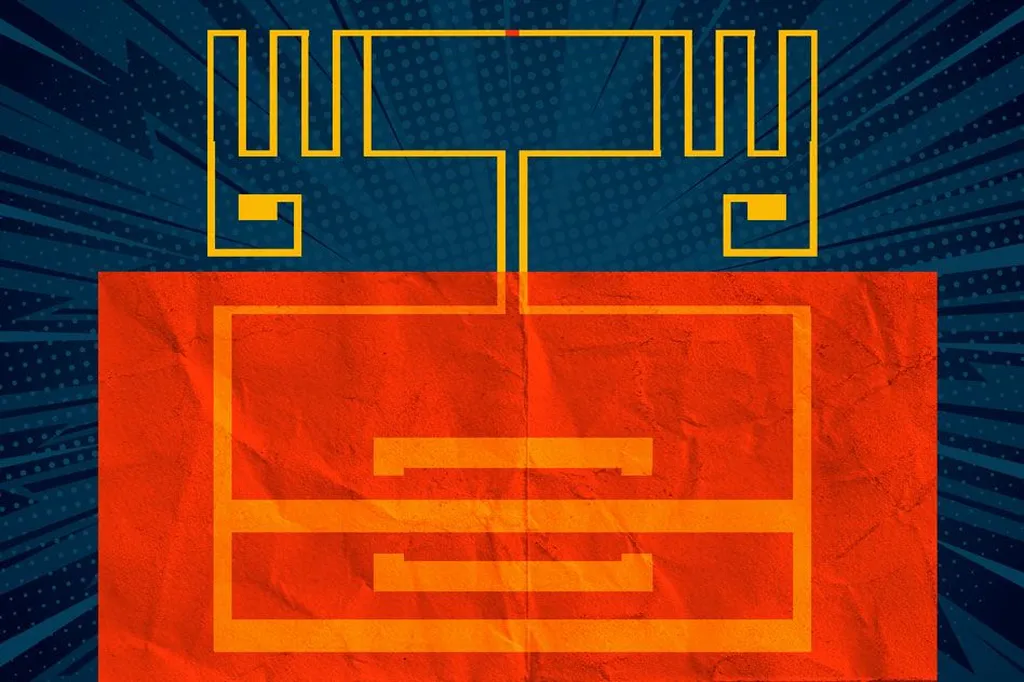
At the heart of this research is Ahmed Kabeel, an assistant professor in the Electronics and Communication Department at the Faculty of Engineering, Delta University for Science and Technology in Egypt. Kabeel and his team have designed a radio frequency energy harvesting (RF-EH) system specifically tailored for the 2.45 GHz Wi-Fi band. The system is composed of three main components: a circular-shaped microstrip antenna array, an equal-power combiner, and an FR-4 based RF-to-DC rectifier circuit.
The antenna array, designed to enhance signal reception, boasts a measured gain of 15.8 dBi. “This is a significant improvement over existing designs,” Kabeel explains. “It allows us to capture more ambient Wi-Fi signals, which are then converted into usable DC power by the rectifier circuit.”
The rectifier circuit, built on an inexpensive FR-4 substrate, offers a peak power conversion efficiency of 24.03% at an input power of 1.3 dBm. This efficiency, combined with the system’s compact size and low cost, makes it an attractive option for powering low-energy wireless devices.
The potential commercial impacts of this research are substantial. As the IoT market continues to grow, so does the demand for efficient, low-cost power solutions for wireless sensors and devices. This RF-EH system could be a game-changer, providing a sustainable and reliable energy source for these devices.
Moreover, the system’s design and implementation could pave the way for future developments in the field of RF energy harvesting. As Kabeel notes, “Our work demonstrates the feasibility of using ambient Wi-Fi signals as a viable energy source. This could inspire further research into other forms of RF energy harvesting, contributing to a more sustainable and connected future.”
The study, titled “Design and Implementation of A Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting (RF-EH) System in the WI-FI Band,” was published in the Journal of Engineering Sciences (JES), which translates to the Journal of Engineering Sciences in English. This research not only advances our understanding of RF energy harvesting but also opens up new possibilities for the energy sector, particularly in the realm of wireless communication applications.