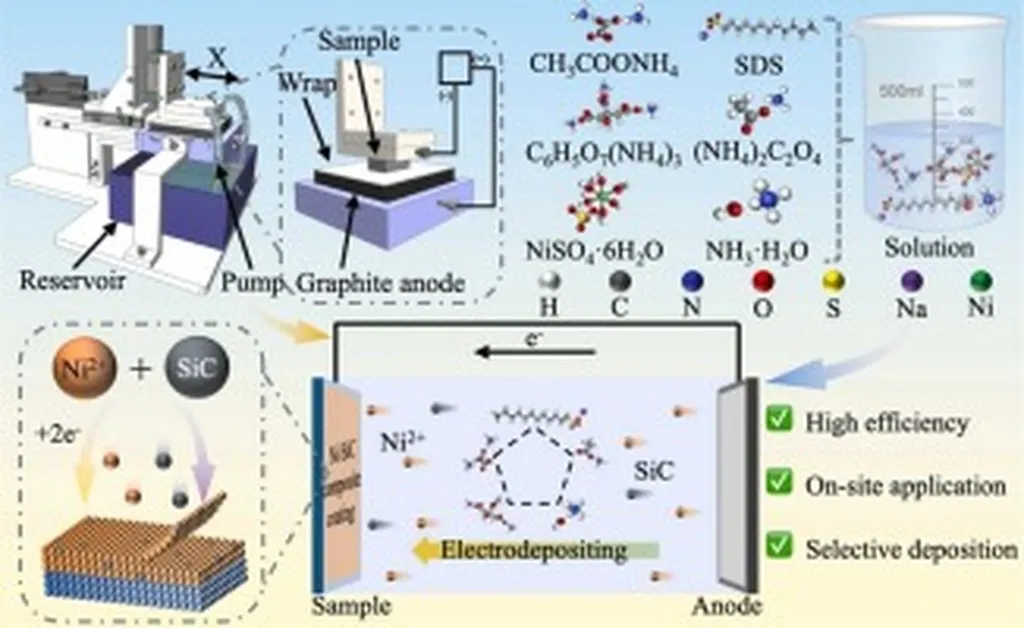
In the quest to bolster the durability and longevity of materials used in harsh environments, a groundbreaking study has emerged that could significantly impact the energy sector. Researchers, led by S. Shanmugam, have delved into the enhancement of Ni-SiC composite coatings on AISI 1018 steel, a material commonly used in various industrial applications. The study, published in the journal *Materials Research* (translated from Portuguese as *Pesquisa em Materiais*), explores the potential of pulse reverse electrodeposition to create more resilient coatings.
The research systematically varied the concentration of nano-Silicon Carbide (nano-SiC) in the composite coatings, ranging from 1% to 5%. The findings revealed a compelling trend: as the concentration of nano-SiC increased, so did the microhardness of the coatings. The highest hardness was achieved with the NHC5 specimen, which contained 5% SiC. This specimen showed a 5.76% increase in hardness compared to its predecessor, NHC4.
“The incorporation of nano-SiC into the nickel matrix not only enhanced the hardness but also significantly improved the corrosion and wear resistance of the composite coatings,” explained Shanmugam. This enhancement is crucial for materials used in the energy sector, where equipment often faces harsh conditions that can lead to rapid degradation.
X-ray diffraction analysis confirmed the successful incorporation of nano-SiC into the nickel matrix, with characteristic SiC peaks observed. This structural integration played a pivotal role in the improved performance of the coatings. The NHC5 coating, in particular, exhibited the lowest corrosion rate and material loss, indicating superior corrosion resistance.
Moreover, the wear performance of the NHC5 coating was remarkable. It showed a 93.12% reduction in specific wear rate and a 62.93% reduction in the coefficient of friction compared to the reference material. Microscopic analysis further corroborated these findings, revealing minimal wear and corrosion damage on the NHC5 specimen.
The implications of this research are far-reaching. In the energy sector, where materials are often subjected to extreme conditions, the enhanced durability and longevity of Ni-SiC composite coatings could lead to significant cost savings and improved safety. The use of these coatings could extend the lifespan of critical components, reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement.
“This study opens up new avenues for the development of advanced materials that can withstand the rigors of industrial applications,” said Shanmugam. The findings could pave the way for future research into other nano-reinforcements and their potential to enhance material properties.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the demand for materials that can perform reliably in challenging environments will only grow. The research published in *Materials Research* provides a promising direction for future developments, offering a glimpse into the potential of nano-reinforced composite coatings to revolutionize the industry.