In the quest to enhance the performance of titanium dioxide (TiO2) in energy applications, a team of researchers from Hebei University of Science and Technology has made significant strides. Led by Dr. Zhou Yuhao, the team has explored the potential of micro-arc oxidation (MAO) to improve TiO2’s efficiency in photocatalysis and electrochemical energy storage, areas critical to the energy sector.
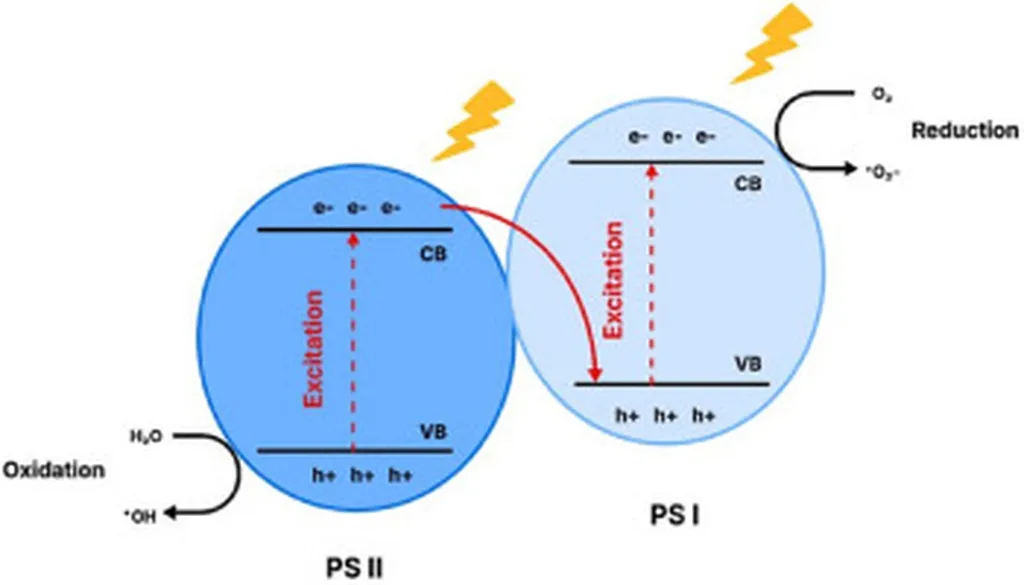
TiO2 has long been recognized for its applications in photocatalysis and energy storage, but it has faced limitations such as high recombination rates of photogenerated charge carriers and poor electrical conductivity. These issues have hindered its performance in lithium-ion batteries and other energy storage devices. The team’s research, published in *Cailiao Baohu* (translated to *Material Protection*), delves into how MAO can address these challenges.
By controlling the electrical parameters and electrolyte composition during the MAO process, the researchers can regulate the composition, phase composition, and surface morphology of the oxide film. This process simplifies the modification process and allows for the in-situ formation of self-supporting porous TiO2 oxide films on the surface of titanium or titanium alloys.
“The key here is the large specific surface area of the TiO2 films prepared via MAO,” explains Dr. Zhou. “This increased surface area can load more active substances, enhancing electrical conductivity and ionic mobility, which in turn improves both catalytic activity and electrochemical energy storage performance.”
The research highlights the potential of MAO technology to open new pathways for TiO2 applications in the energy sector. By improving the performance of TiO2 in lithium-ion batteries and other energy storage devices, this technology could contribute to more efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
Dr. Zhou and his team also explored the effects of electrolyte composition, electrical parameters, and oxidation time on the morphology, phase composition, optical properties, and electrochemical performance of TiO2. Their findings suggest that MAO technology could play a crucial role in the future of energy storage and photocatalysis.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the need for efficient and sustainable materials becomes increasingly important. The research conducted by Dr. Zhou and his team at Hebei University of Science and Technology offers a promising avenue for enhancing the performance of TiO2, potentially shaping the future of energy storage and photocatalysis.
The team’s work not only advances our understanding of TiO2’s potential but also underscores the importance of innovative technologies like MAO in addressing the challenges faced by the energy sector. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, such advancements could prove instrumental in meeting global energy demands.