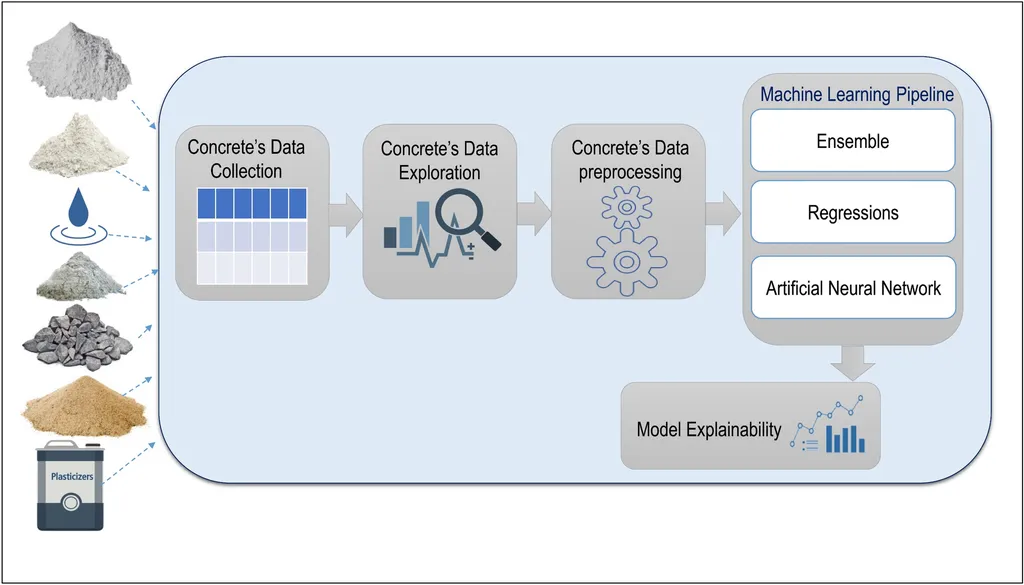
In the world of construction, precision is paramount, and nowhere is this more critical than in the estimation of concrete compressive strength. A recent study published in the journal *Civil and Environmental Engineering* (translated from Chinese as “土木环境工程”) has introduced a groundbreaking approach that could revolutionize how we predict this essential metric. Led by Xiong Jiangyu of the School of Civil and Transportation Engineering at Qinghai Minzu University in Xining, China, the research leverages Bayesian optimization to fine-tune neural networks, offering a significant leap in predictive accuracy.
Concrete compressive strength is a cornerstone of quality control in construction engineering. Traditional methods, such as empirical formulas and regression models, often fall short in capturing the complex, nonlinear relationships between various factors. Neural networks, while powerful, can suffer from hyperparameter sensitivity and overfitting, leading to less reliable predictions. Xiong Jiangyu and his team addressed these challenges by developing a Bayesian-optimized fully connected neural network (BOFCNN). This innovative model uses Gaussian process surrogate modeling to dynamically identify optimal hyperparameters, such as learning rate and neuron count, thereby enhancing the model’s generalization capability.
The study utilized 1,015 experimental datasets from the UCI repository. To refine the model further, the researchers integrated feature selection techniques, combining Pearson-Spearman correlation with random forest importance ranking. The results were impressive: the optimized model achieved a mean squared error (MSE) of 21.0745 MPa², an R² value of 0.9080, and a mean absolute error (MAE) of 3.5028 MPa. Within the primary strength range of 10–60 MPa, the predictions showed strong agreement with experimental data, confirming the efficacy of Bayesian optimization in enhancing predictive accuracy.
“This research establishes a robust computational framework for concrete strength prediction,” Xiong Jiangyu explained. “By optimizing the neural network’s hyperparameters, we can achieve more accurate and reliable predictions, which is crucial for sustainable mix design optimization.”
The implications of this research are far-reaching, particularly for the construction and energy sectors. Accurate prediction of concrete compressive strength is essential for ensuring the durability and safety of structures, from skyscrapers to energy infrastructure. By providing a more precise and efficient method for estimating this critical metric, the BOFCNN model can help engineers and architects make informed decisions, ultimately leading to more sustainable and cost-effective construction practices.
“Our goal is to push the boundaries of what’s possible in construction engineering,” Xiong Jiangyu added. “By leveraging advanced computational techniques, we can develop more accurate models that will shape the future of the industry.”
As the construction industry continues to evolve, the integration of advanced technologies like Bayesian optimization and neural networks will play a pivotal role in driving innovation. This research not only highlights the potential of these techniques but also sets the stage for future developments in the field. By embracing these advancements, the industry can achieve greater precision, efficiency, and sustainability, ultimately benefiting both the environment and the bottom line.
In the quest for better, more accurate predictions, Xiong Jiangyu and his team have made a significant stride. Their work not only advances the field of construction engineering but also offers a glimpse into the future of sustainable and efficient building practices. As the industry continues to grow and evolve, the insights gained from this research will undoubtedly shape the way we build, ensuring a stronger, safer, and more sustainable world for generations to come.