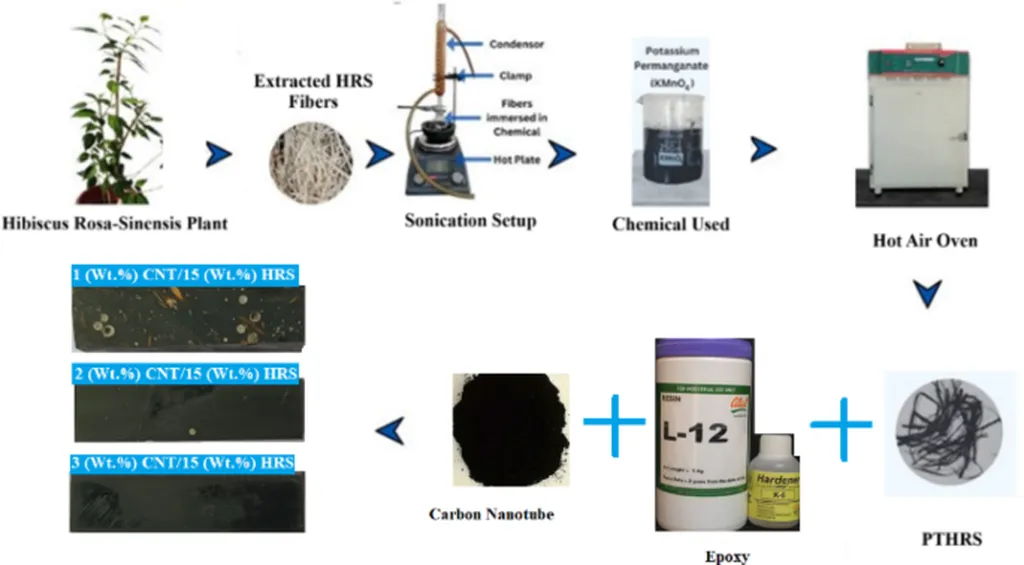
In a groundbreaking study published in the journal *Materials Research Express*, researchers have unveiled a novel approach to enhancing the thermal properties of polymer composites, with significant implications for the energy sector. The study, led by Supriya J P from the Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering at Manipal Institute of Technology, focuses on the thermal characteristics and combustion behavior of hybrid composites made from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (HRS), carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and epoxy.
The research demonstrates that by optimizing the weight percentage, diameter, sonication time, and thickness of CNTs in the composite, it is possible to achieve remarkable improvements in thermal conductivity and flame resistance. “We found that a 3% weight percentage of CNTs significantly boosts thermal conductivity, reaching a maximum value of 0.985 W m^−1·K,” explains Supriya J P. “This enhancement is due to the effective formation of a CNT network that facilitates efficient heat transfer and increases thermal stability.”
The study also reveals that larger CNT diameters, specifically 3 nm, contribute to improved thermal and flame-retardant properties, reducing the burning rate to 5.18 mm min^−1 compared to 11 mm/min for composites with 1% CNT and 1 nm diameter. Optimal sonication time at 60 minutes ensures uniform CNT dispersion within the polymer matrix, further enhancing thermal conductivity and reducing burning rates. Additionally, thicker composites (20 mm) exhibit lower burning rates and higher thermal degradation temperatures, making them more effective thermal barriers.
One of the most compelling aspects of this research is the application of a backpropagation artificial neural network (BPANN) for predicting the thermal properties of the composites. The BPANN model achieved a negligible error of 0.15%, compared to a 0.68% error for response surface methodology (RSM) predictions. This advanced computational technique not only validates the experimental results but also provides a powerful tool for designing and optimizing polymer composites with tailored thermal and combustion properties.
The implications of this research for the energy sector are profound. The development of high-performance polymer composites with enhanced thermal stability and flame resistance opens up new possibilities for applications in high-temperature environments, such as in energy storage systems, thermal insulation, and fire-resistant materials. “This research provides valuable insights into the design and optimization of polymer composites with tailored thermal and combustion properties, offering potential applications in fields requiring high thermal stability and flame resistance,” says Supriya J P.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the demand for materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and provide superior thermal management is growing. The findings of this study not only advance our understanding of the thermal properties of polymer composites but also pave the way for innovative solutions that can meet the challenges of the future. With the publication of this research in *Materials Research Express* (which translates to “Expressions of Materials Research”), the scientific community now has a robust framework to build upon, potentially revolutionizing the way we design and utilize materials in energy-related applications.