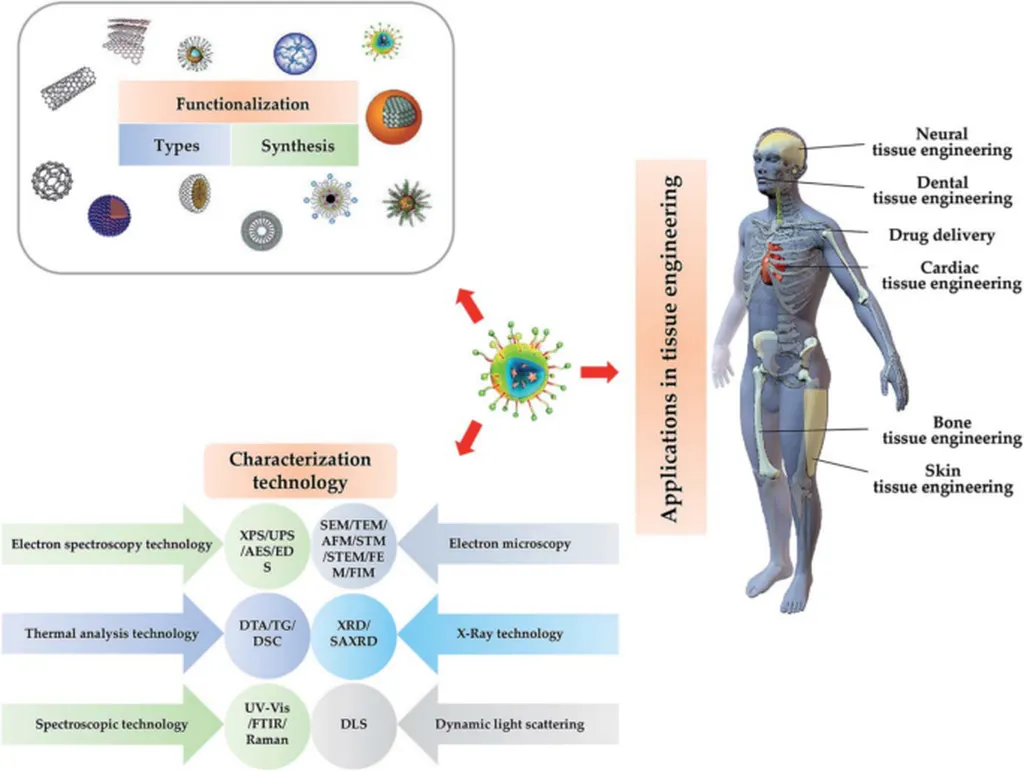
In the bustling intersection of medicine and engineering, a groundbreaking study published in *SmartMat* (translated from Chinese as “Intelligent Materials”) is poised to revolutionize how we approach tissue repair and stem cell differentiation. Led by Xiao Han from the Department of Neurosurgery at Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University in Jinan, China, the research delves into the transformative potential of external-field-driven functional nanomaterials.
The study highlights the limitations of traditional biological and chemical signals in regulating stem cell differentiation, emphasizing the need for more precise and tunable methods. “Macroscopic external physical fields alone are generally ineffective for modulating stem cell fate,” explains Han. “However, nanostructure-mediated physical signals offer a novel approach by generating localized, quantifiable, and dynamically controllable cues.”
These cues, recognized by cell surface receptors, can regulate stem cell differentiation through nanoscale extracellular matrix components like fibrin and polysaccharide fibers. The core mechanisms involve field-induced material polarization, nanostructure-mediated signal amplification, energy conversion effects, and synergistic activation of downstream gene expression.
The implications of this research extend far beyond the medical field, with significant commercial impacts for the energy sector. The development of functional nanomaterials that respond to external fields could lead to more efficient energy storage and conversion systems. Imagine nanomaterials that can be precisely controlled to enhance the performance of batteries, solar cells, and other energy technologies.
“This interdisciplinary approach not only synthesizes the mechanisms and effects of diverse nanostructure-mediated physical signals but also inspires further collaboration in engineering-medicine applications,” says Han. The study’s novel concept—”regulation of stem cell fate via nanostructure-mediated physical signals”—is set to become a critical frontier in biomaterials, cell biology, and tissue engineering.
As we stand on the brink of this technological revolution, the research published in *SmartMat* offers a glimpse into a future where the boundaries between disciplines blur, and innovative solutions emerge to address some of the most pressing challenges in medicine and energy. The collaboration between engineers, scientists, and medical professionals promises to unlock new possibilities, driving progress and shaping the future of these interconnected fields.