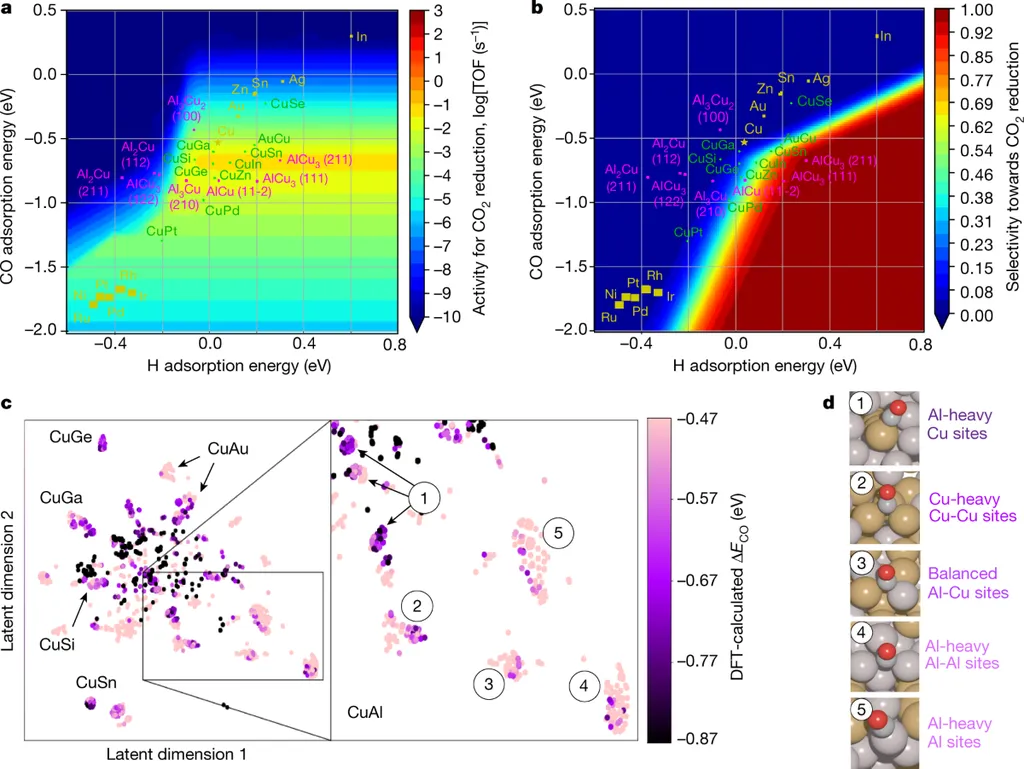
In a groundbreaking development poised to reshape the energy sector, researchers have harnessed the power of artificial intelligence to accelerate the discovery of electrocatalyst materials, a critical component in technologies like fuel cells and electrolyzers. The study, led by Yifan Zeng from the Sydney AI Centre at the University of Sydney, marks a significant stride towards more efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
Electrocatalysts are materials that facilitate chemical reactions in electrochemical devices, playing a pivotal role in clean energy technologies. However, the traditional process of discovering and developing these materials has been time-consuming and costly. Zeng and his team have tackled this challenge by employing AI to predict and identify promising electrocatalyst materials at an unprecedented pace.
“The integration of AI in materials science is revolutionizing the way we approach research and development,” said Yifan Zeng, lead author of the study. “By leveraging machine learning algorithms, we can significantly reduce the time and resources required to identify potential electrocatalysts, paving the way for more rapid innovation in the energy sector.”
The research, published in ACS Materials Au (which translates to American Chemical Society Materials Gold), demonstrates the potential of AI to transform the landscape of materials discovery. The team’s approach involves training AI models on vast datasets of known materials and their properties, enabling the models to predict the performance of new, unexplored materials as electrocatalysts.
“This study is a testament to the power of interdisciplinary collaboration,” added Zeng. “By combining expertise in computer science, materials science, and chemical engineering, we can tackle complex challenges and drive advancements that have real-world impacts.”
The implications of this research are far-reaching for the energy sector. Efficient electrocatalysts are crucial for improving the performance and reducing the cost of technologies like hydrogen fuel cells and water electrolyzers, which are key to a sustainable energy future. The AI-accelerated discovery process could lead to the development of new materials that enhance the efficiency and durability of these technologies, making them more viable for large-scale deployment.
Moreover, the methodology developed by Zeng and his team can be applied to other areas of materials science, potentially accelerating the discovery of materials for various applications, from batteries to semiconductors. This interdisciplinary approach not only speeds up the research process but also fosters innovation by identifying materials that might otherwise have been overlooked.
As the world continues to seek sustainable energy solutions, the role of AI in materials discovery becomes increasingly vital. The work of Yifan Zeng and his team at the Sydney AI Centre represents a significant step forward in this endeavor, offering a glimpse into a future where AI-driven innovation propels the energy sector towards a cleaner and more efficient tomorrow.