In the ever-evolving landscape of cardiovascular interventions, a groundbreaking study led by Buse Durak from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Izmir Katip Celebi University in Türkiye is poised to revolutionize the way we approach vascular stent technology. Published in the esteemed journal *Academia Materials Science* (translated from Turkish as “Academia of Materials Science”), this research introduces a novel bilayer nanofiber coating that promises to enhance the biological performance of vascular stents, addressing critical challenges such as thrombus formation, oxidative stress, and inadequate endothelialization.
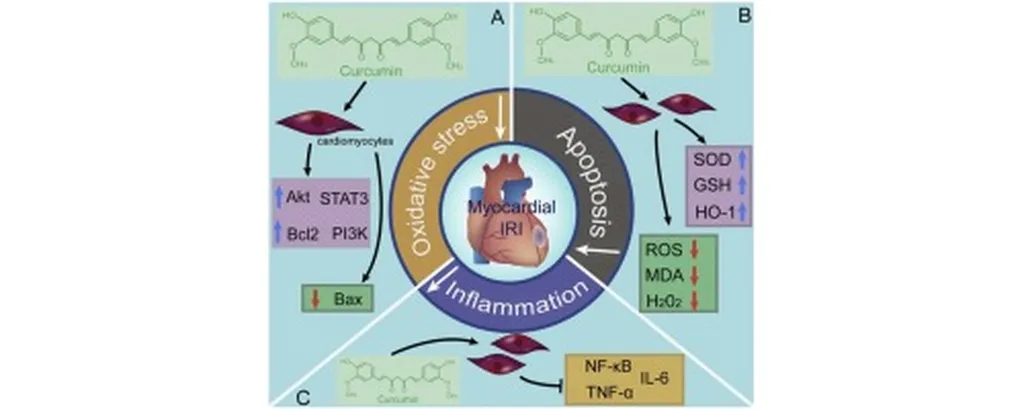
The study focuses on the design and in vitro assessment of a curcumin-eluting bilayer poly(lactic acid)/hyaluronic acid (PLA/HA) nanofiber coating. This innovative approach aims to improve the long-term success of cardiovascular stent implantation by incorporating curcumin, a compound known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. “Our goal was to create a multifunctional platform that not only supports endothelialization but also enhances antioxidant protection and blood compatibility,” Durak explained.
The research team characterized the physicochemical properties, wettability, and water absorption of the coatings, ensuring that the functional performance met the necessary standards. Curcumin loading efficiency, degradation behavior, and antioxidant activity were thoroughly assessed. The results were promising, with curcumin efficiently loaded in all groups and showing minimal degradation over 28 days. The incorporation of curcumin significantly enhanced hydrophilicity and increased water absorption capacity, which are crucial factors for optimal stent performance.
One of the most compelling aspects of this study is the evaluation of hemocompatibility and cytocompatibility. Using L929 and HUVEC cell lines, the researchers verified cellular responses relevant to vascular healing. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) displayed high viability and adherence to the bilayer coatings, supported by fluorescence staining. This indicates that the coatings provide favorable topography and biochemical cues for cellular attachment and growth.
The study also demonstrated a significant reduction in reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, highlighting the improved antioxidant efficacy of the curcumin-eluting coatings. Both curcumin-blended and curcumin-free PLA/HA nanofiber coatings exhibited excellent hemocompatibility, with hemolysis below 0.5%. Anti-thrombotic assays of curcumin-blended stents showed stable performance under simulated in-practice conditions, further underscoring their potential as advanced coatings for cardiovascular stents.
The implications of this research are far-reaching, particularly for the energy sector, where cardiovascular health is a critical concern. As the population ages and lifestyle-related cardiovascular diseases become more prevalent, the demand for advanced stent technologies is on the rise. This innovative coating technology could significantly improve patient outcomes and reduce the need for costly and invasive follow-up procedures.
Durak and her team’s work not only addresses immediate clinical needs but also paves the way for future developments in the field. “This research opens up new avenues for exploring the potential of natural compounds like curcumin in biomedical applications,” Durak noted. The successful integration of curcumin into nanofiber coatings could inspire further studies on the use of other bioactive compounds to enhance the performance of medical devices.
In conclusion, the study published in *Academia Materials Science* represents a significant step forward in the quest for improved vascular stent technology. By combining the antioxidant properties of curcumin with the biocompatibility of PLA/HA nanofiber coatings, Durak and her colleagues have created a multifunctional platform that holds great promise for the future of cardiovascular interventions. As the energy sector continues to evolve, the adoption of such advanced technologies could play a pivotal role in enhancing patient care and improving overall health outcomes.