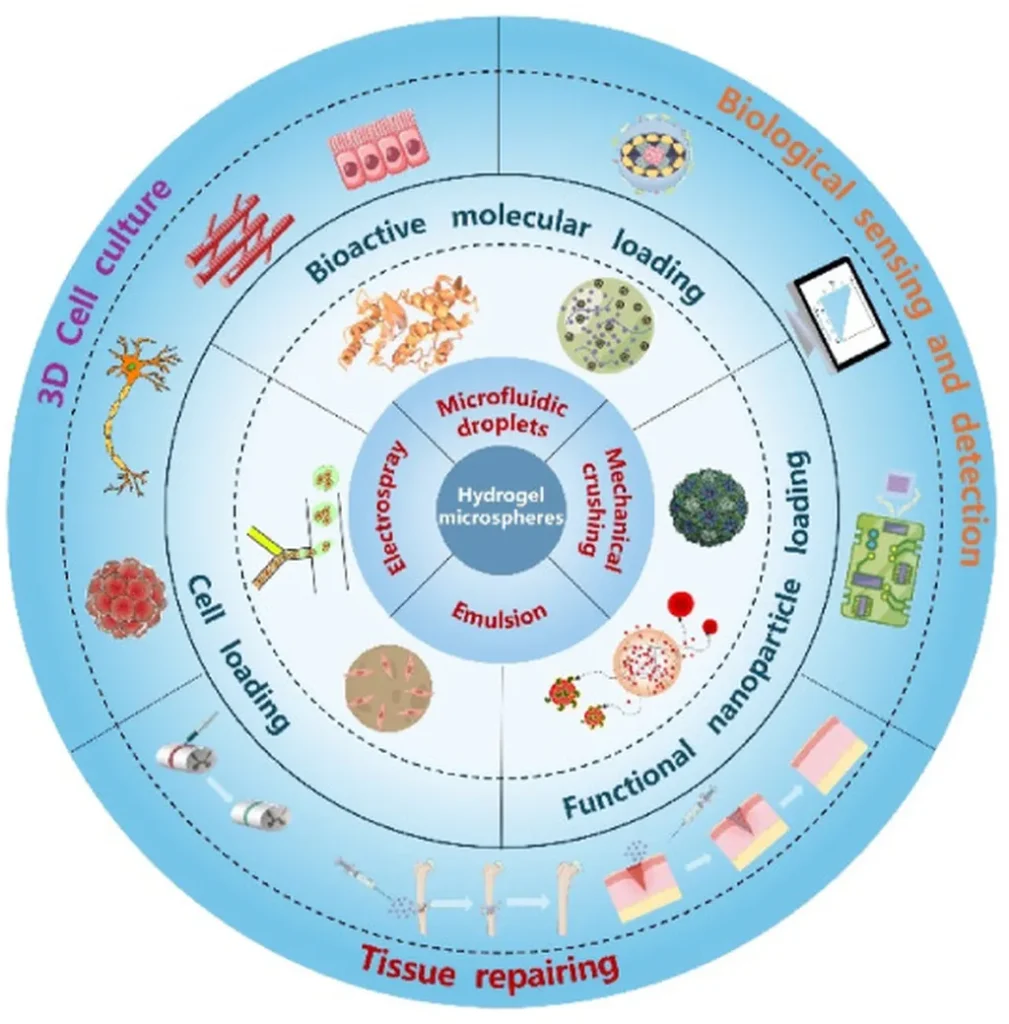
In the bustling world of biomedical research, a new player has emerged, promising to revolutionize the way we approach various medical challenges. Hydrogel microspheres (HMs), tiny spheres of hydrogel, are capturing the attention of scientists and industry professionals alike, thanks to their versatile applications in drug delivery, cell culture, regenerative medicine, wound healing, and even tumor immunity. This cutting-edge research, led by Yingkang Huang from the Department of General Surgery at The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University in Suzhou, China, is paving the way for innovative solutions in the biomedical field.
Hydrogels, a network of polymer chains that can absorb and retain large amounts of water, have been a subject of interest for years. However, the recent focus on hydrogel microspheres represents a significant shift in the field. “HMs offer unique structural and functional advantages,” explains Huang. “They can be composed of diverse biobased materials and fabricated through various preparation methods, making them highly versatile for different biomedical applications.”
The potential of HMs is vast. In drug delivery, for instance, these microspheres can encapsulate drugs and release them in a controlled manner, improving the efficacy and reducing the side effects of treatments. In regenerative medicine, HMs can serve as scaffolds for cell growth, promoting tissue regeneration and repair. Moreover, their application in wound healing and tumor immunity is opening up new avenues for research and development.
The commercial impacts of this research are substantial. The global hydrogel market is projected to reach $23.4 billion by 2025, with biomedical applications being a significant driver of this growth. The development of HMs could further boost this market, creating new opportunities for companies involved in drug delivery, medical devices, and regenerative medicine.
However, the journey from the lab to the clinic is not without its challenges. As Huang notes, “While the therapeutic potential of HMs is promising, there are still many hurdles to overcome, such as optimizing their preparation methods and ensuring their safety and efficacy in clinical settings.”
Published in the journal ‘Small Science’ (translated from Chinese as ‘小科学’), this research consolidates current knowledge and highlights emerging trends and challenges in the field of HMs. By doing so, it aims to inspire further research and accelerate the clinical translation of these innovative microspheres.
As we look to the future, the potential of hydrogel microspheres in the biomedical field is immense. With continued research and development, these tiny spheres could play a significant role in shaping the future of medicine, offering new hope for patients and new opportunities for the industry. The story of HMs is just beginning, and it’s one that we’ll be watching closely in the coming years.