In the relentless battle against arboviral infections, a beacon of hope emerges from the world of nanotechnology. Researchers, led by Peyman Halvaeikhanekahdani from the Queensland Quantum and Advanced Technologies Research Institute (QUATRI) at Griffith University, have published a comprehensive review in *Nano Select* (which translates to *Nano Choice*), outlining the potential of dual-function nanoparticle platforms for both diagnosing and vaccinating against these viral threats.
Arboviruses, such as dengue, Zika, and yellow fever, pose significant global health challenges, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. Current diagnostic methods often fall short due to delays and limited sensitivity, while vaccine rollouts can be slow and fragmented. Halvaeikhanekahdani and his team have been exploring how nanotechnology can bridge these gaps, offering highly sensitive biosensors and effective vaccine delivery platforms.
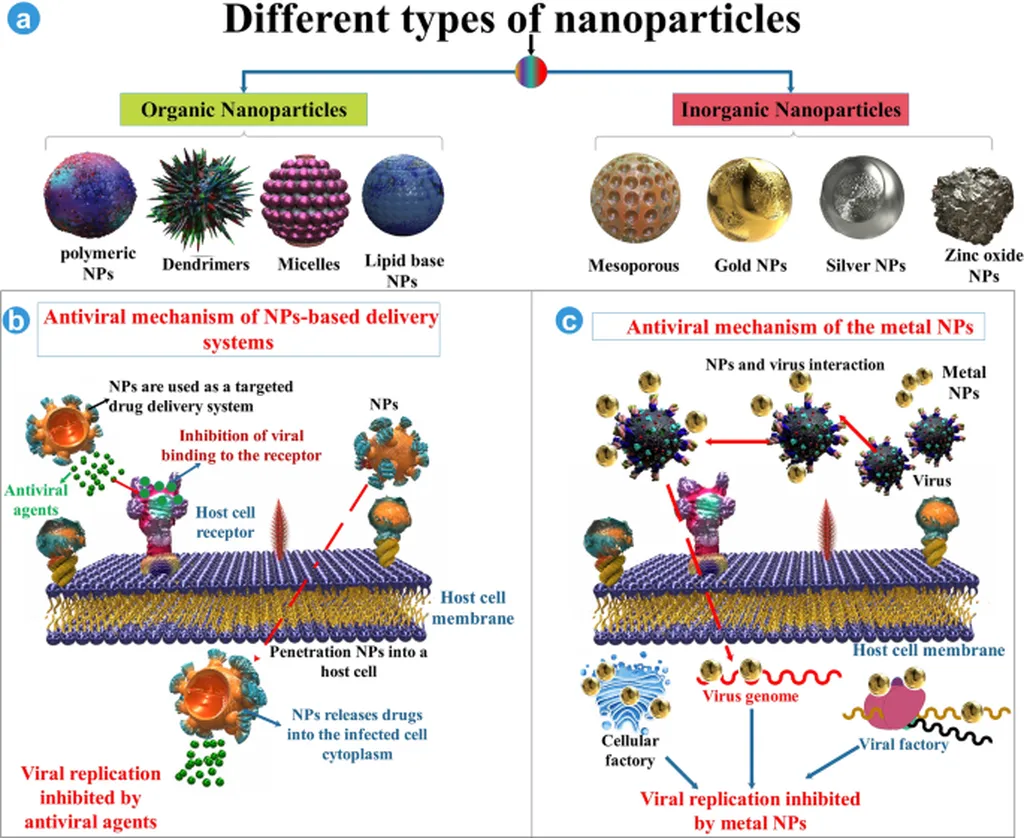
The review highlights several top-performing nanoparticles, including gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs), molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanocomposites, and lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). These nanoparticles have shown promise in both detecting viruses and delivering vaccines, but until now, no single platform has combined both functions.
“By integrating diagnostic and vaccine capabilities into a single nanoparticle platform, we could revolutionize outbreak control,” Halvaeikhanekahdani explained. “This approach could be particularly crucial in resource-limited regions where coendemic viruses are a persistent threat.”
The potential commercial impacts for the energy sector, while not directly addressed in the study, could be significant. For instance, in regions where arboviral outbreaks are common, having a rapid, point-of-care diagnostic and vaccination tool could minimize disruptions to the workforce, ensuring continuity in energy production and distribution. Additionally, the technology could be adapted for other industries where worker health is paramount, such as construction and agriculture.
The review also underscores the challenges that lie ahead. Developing a universal nanoparticle platform that can effectively detect and vaccinate against multiple arboviruses is a complex task. However, the progress made so far suggests that this goal is within reach.
As the world continues to grapple with emerging viral threats, the work of Halvaeikhanekahdani and his team offers a glimpse into a future where rapid diagnosis and immunization could become a reality. Their findings, published in *Nano Select*, not only advance our understanding of nanotechnology’s potential in public health but also pave the way for innovative solutions that could protect communities and industries alike.
In the words of Halvaeikhanekahdani, “This dual-function design approach has the added benefit of bridging a crucial gap in current diagnostic capabilities and prevention. It serves as a foundation for next-generation nanoenabled public health tools for rapid response and sustained protection against arboviral threats.”