In a significant stride towards enhancing fuel cell technology, researchers have developed a novel nanocomposite membrane that could revolutionize the energy sector. The study, led by Maryam Oroujzadeh from the Polymer Science Research Institute at Iran’s Polymer and Petrochemical Institute, focuses on integrating sulfonated graphene oxide (sGO) nanosheets into sulfonated poly(arylene ether) (sPAE) membranes. This innovation aims to boost the efficiency and performance of proton exchange membranes (PEMs) in polymer electrolyte fuel cells.
Fuel cells are critical components in the clean energy landscape, converting chemical energy into electricity with high efficiency and low emissions. However, their widespread adoption has been hindered by the limitations of current PEMs, particularly their proton conductivity and durability. Oroujzadeh’s research addresses these challenges head-on. “The incorporation of sulfonated graphene oxide into the polymer matrix significantly enhances the membrane’s physicochemical and electrochemical properties,” Oroujzadeh explains. “This improvement is crucial for the next generation of fuel cells, which demand higher performance and longevity.”
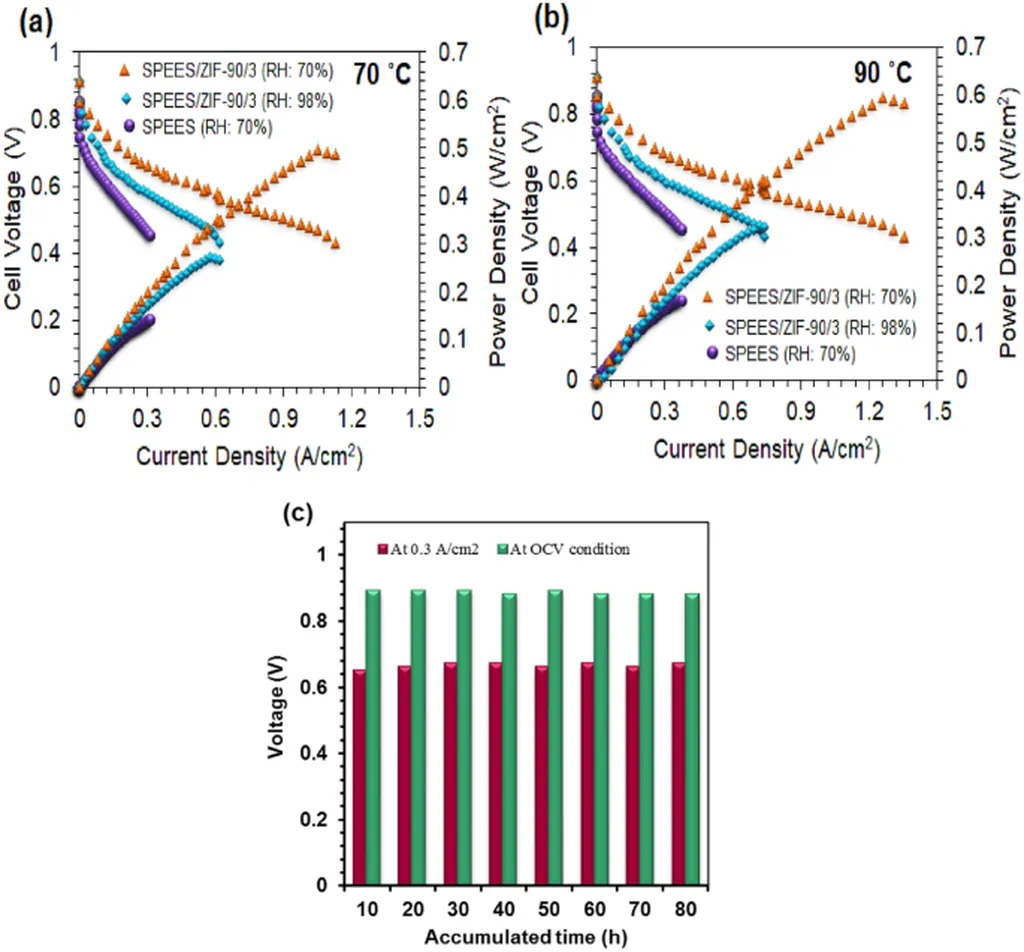
The research team prepared nanocomposite membranes by introducing sGO nanoparticles into the sPAE matrix at varying weight percentages. The optimal composition was found to be 2 wt% sGO, which exhibited remarkable properties. This membrane achieved an ion exchange capacity of 1.98 meq/g, ensuring efficient proton transfer. It also demonstrated a water uptake of 31.8%, striking a balance between hydrophilicity and structural integrity. Proton conductivity at 80 °C reached an impressive 0.268 S/cm, a key metric for fuel cell performance.
In single-cell fuel cell tests at 80 °C, the 2 wt% sGO membrane showed a 15% increase in current density and a 30% increase in power density compared to the pristine membrane. These results underscore the potential of sGO-modified sPAE membranes to significantly enhance fuel cell efficiency and performance.
The implications of this research are far-reaching for the energy sector. As the world shifts towards sustainable energy solutions, the demand for efficient and reliable fuel cells continues to grow. “This study opens up new avenues for developing advanced materials that can meet the stringent requirements of modern fuel cells,” Oroujzadeh notes. “The enhanced performance of these membranes could accelerate the adoption of fuel cells in various applications, from transportation to stationary power generation.”
The study, published in the Journal of Advanced Materials in Engineering (known in English as the Journal of Advanced Materials in Engineering), highlights the importance of interdisciplinary research in driving technological advancements. By combining materials science, chemistry, and engineering, Oroujzadeh and her team have made a significant contribution to the field of energy storage and conversion.
As the energy sector continues to evolve, the development of high-performance fuel cell membranes will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of clean energy. This research not only advances our understanding of nanocomposite materials but also paves the way for more efficient and sustainable energy solutions. The potential commercial impacts are substantial, with the promise of more reliable and cost-effective fuel cells that could power everything from electric vehicles to grid storage systems. The future of energy is bright, and innovations like these are leading the way.